Memory “rasp-mem”
RASP memory plug-in is the main store (operating memory) used in RASP virtual computer. RASP is an example of von-Neumann architecture, which implies that both program and data reside in the same memory.
After compilation of a RASP source code, the compiled program is loaded into RASP memory. During the process of the emulation, the CPU plug-in reads instructions and their operands from the memory and writes results back to the same memory (except reading inputs and writing outputs).
Graphical user interface (GUI)
RASP memory has a simple window, which can be accessed from the debug panel in emuStudio:
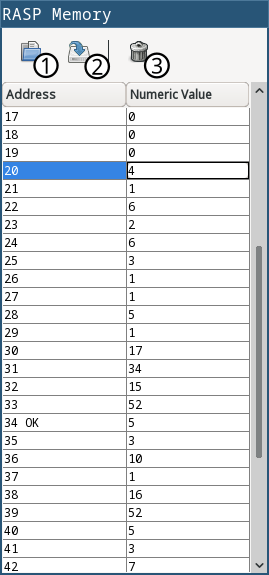
| 1 | Open already compiled program into memory. The previous program will be dismissed. RASP binary files has extension .brasp. |
| 2 | Dump memory content into a file (either human-readable or .brasp). |
| 3 | Clears memory. |
The table with memory content is editable. By double-clicking on a row you can simply edit the value. You confirm your changes by the ENTER key:
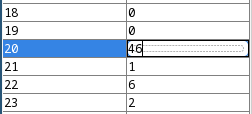
NOTE: By editing an opcode cell (a cell that contains an instruction opcode), the instruction is changed. It is also possible to set invalid opcode values, which then results in “address fallout” error during emulation.
For example, if a cell contains the ADD = instruction (operation code 7), which is then changed to 9 (SUB =), the instruction on that location will be now changed and emuStudio will interpret it as such.